Abstract: Sustainability largely depends on four major pillars: human, social, economic, and environmental. Any industry can be sustained if the products are of satisfactory quality at a suitable price. Key to this is good raw materials, efficient conservation practices, skilled workers, and effective teamwork. Proper cost control, minimizing waste, and adopting the “reduce, reuse, recycle” mindset are also crucial for sustainability. Recycling and energy efficiency are vital components of a sustainable industry. However, poor management and power struggles within an organization can undermine efforts towards sustainability. A clear ethical framework, effective leadership, and respect for all members within an organization are essential to achieving long-term sustainability. This paper explores the significance of human resources, team dynamics, and proper management for ensuring sustainability, particularly in the textile industry.
Keywords: Products, Quality, Human Resources, Waste Reduction, Power Struggles, Sustainability
1. Introduction: Sustainability is a multifaceted concept that depends on human resources, social structure, economic stability, and environmental conservation. These four pillars support the foundation for any industry to remain viable in the long term. In particular, the textile industry, which is a significant global economic force, requires attention to quality raw materials, skilled labor, and efficient management systems. When the quality of the workforce is poor, even the best raw materials and equipment cannot ensure sustainable success. As the author argues, “Flashy positions are temporary, species and titles are limited, but the way you treat people will always be remembered.”
The pillars of sustainability — people, planet, and profits — are interconnected. To ensure sustainability, a business must conserve natural resources, support healthy communities and employees, and remain financially viable. A company’s ability to uphold these values, while driving profitability and innovation, is crucial for long-term survival. A negative attitude or lack of commitment from employees can undermine these efforts. Therefore, strong organizational leadership, a committed workforce, and a solid ethical framework are essential to achieving true sustainability.
- Quality, Profitability, and Sustainability
The relationship between quality, profitability, and sustainability is especially important in the textile industry. Profitability is directly tied to the customer’s satisfaction with the product quality and its price. High-quality products offered at a competitive price will lead to increased sales, which in turn drives profitability and supports sustainability. However, this is not solely the responsibility of individual workers; it requires teamwork, cooperation, and leadership.
A strong team with a clear vision is essential for driving the industry forward. If management lacks transparency or exhibits unethical behavior, such as bribery or monopolistic control, it can derail efforts to maintain product quality, even if the organization invests heavily in raw materials and skilled labor. Effective management structures and transparent leadership are vital to achieving the industry’s targets. Disunity and power struggles within management can render the efforts futile. For sustainability to thrive, team spirit, ethical values, and leadership are essential.
- Key Elements for Sustainability in the Textile Industry
The following strategies are critical for ensuring the sustainability of the textile industry:
Zero Waste Initiative
One of the key principles for sustainability is the “reduce, reuse, and recycle” framework. In textile production, waste reduction is paramount. Processes must be optimized to ensure that raw materials are used efficiently, and any waste generated must be minimized. Recycling, especially of synthetic fibers, should be encouraged, and efforts should be made to reclaim waste products for reuse in the production process.
Energy and Water Conservation
The textile industry is notorious for its high water and energy consumption. To make the industry more sustainable, businesses should adopt technologies that reduce water and energy usage. For example, water-saving dyeing techniques and energy-efficient machinery can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of textile production.
Use of Ethical and Sustainable Materials
Another important step towards sustainability is the use of eco-friendly materials. Organic cotton, biodegradable fibers, and recycled fabrics can replace conventional materials that are harmful to the environment. Additionally, products made from sustainable materials, such as eco-friendly synthetics or recycled plastic, should be prioritized.
Ethical Workforce Practices
Sustainability goes beyond environmental concerns and extends to ethical labor practices. Fair wages, safe working conditions, and skill development programs for employees are all critical factors in ensuring a sustainable workforce. Ensuring that the workforce is treated ethically and fairly contributes to the long-term stability of an organization.
Innovation in Processes
Innovative technologies can improve sustainability in numerous ways. Innovations in textile production, such as waste-free design processes, digital printing technologies, and low-water dyeing techniques, are key to reducing the environmental impact of the industry. By continually evolving and incorporating new technologies, the industry can stay competitive while remaining environmentally responsible.
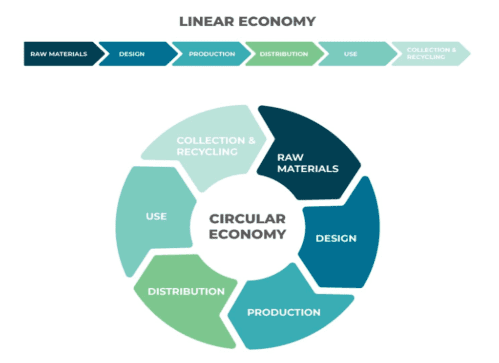
Picture – 1, Circular Economy
In indirect frugality, all the products and the accoutrements are kept in rotation through the methodical process parameters like right conservation, and exercise, to make the ministries in further useful stage in remanufacturing or to make it further usable, reclaim, and to help in growing of the globes with the enrichment of the soils from the naturally degraded accoutrements. It’s the system where the accoutrements no way come to waste and nature is regenerated. Indeed, the machine canvases, after the conservation are thrown in the gutters creating pollution hazards, but now Recycled motor oil painting can be burned as energy, generally in factory boilers, space heaters, or artificial heating operations similar to blast furnaces and cement kilns. When used motor oil painting is burned as energy it must be burned at high temperatures to avoid gassy pollution. Alternately, waste motor oil painting can be distilled into diesel energy or marine energy in a process analogous to oil painting-refining, but without the final hydrotreating process.
- Circular Economy and Sustainability
A circular economy is central to the concept of sustainability. In a circular economy, products and materials are continuously reused and recycled, ensuring that they do not end up as waste. This system promotes the regeneration of natural systems, reducing the need for virgin raw materials and minimizing pollution.
In the textile industry, the circular economy can be applied by reusing fabrics, recycling old clothes into new textiles, and developing processes that allow for the regeneration of materials. For example, used motor oil can be recycled and used as energy in industrial processes, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing waste.
The circular economy model also emphasizes the need for proper waste management, especially in textile production, where large quantities of fabric scraps and dye waste are generated. With proper waste control systems in place, these by-products can be recycled into new materials or used in other industries, thus reducing their environmental impact.
- Innovation and Research
Innovation is the driving force behind sustainability. New ideas, technologies, and processes can improve the efficiency and sustainability of the textile industry. The adoption of eco-friendly and cost-effective technologies is crucial in achieving long-term sustainability.
Research and development in the textile sector should focus on improving product processes, machinery, marketing, and business models. Innovations such as water-saving dyeing techniques, and biodegradable fabrics.
6) Conclusion: Several exploration workshops are going on in sustainability, and my paper is a small part of it. My main area of concern is to form the proper platoon in any working place to achieve the target else the whole investment will go in for the simple waste. The specialized effects mentioned in my paper aren’t new and known to all. But to reach the target, platoon spirit with zeal is a must.

