Its height can reach 1.5 meters. We need 100 to 150 centimeters of rainfall and ideal temperatures between 22 and 32 degrees Celsius. This climate is common in coastal areas and grows well in tropical and subtropical countries during the rainy season. Bromeliad cultivation began in Central and South America and spread throughout the world. One kilogram of leaves can produce 15 to 18 delicious, white, glossy, filamentous buds, 60 cm long. In India alone, fiber production is around 6 tonnes per year. In 2017, global pineapple leaf fiber production was 1.318 million tons.
Process of Pineapple fiber
- Selection of pineapple leaf
Fibers from young leaves are soft and fragile. On older leaves, especially on plants grown in the open air rather than in the shade, short, brittle fibers will appear. So to get strong and flexible fibers, strong, mature plants should have fibers in the areas where their leaves grow.
- Extraction of pine leaf fiber
Peeling machine : This machine is used to peel pineapple leaves. This device has three rollers, namely the feed roller, which is used to feed sheets into the machine; a leaf wood roller, loosens the top layer of the leaf and removes the waxy layer; and a serrated roller, which crushes the leaves.
- Retting of pine leaf
In this process, scraped leaves are bundled and immersed in a sliding tank containing urea and diammonium phosphate. Many chemical components such as pentosan, lignin, fat, wax, ash content, pectin and nitrogenous substances can be extracted. After drying, the leaves are removed, machine washed in fresh water, air dried and hung.
- Degumming of pineapple leaves
Pineapple leaf fiber is composed of fibers that make the fiber brittle and rough, varying between 25 and 35 denier, so water must be removed to make the fiber soft and smooth. Pineapple leaf fibers were found to have a density of 12 to 20 after resin reduction.
- Chemical modifications
Acid treatment or mercerization using sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is the most common treatment method to clean and clean the surface of natural fibers to produce high quality fibers. NaOH reacts with the hydroxyl groups of the natural fiber binders, destroying the cell structure and turning the fibers into filaments.
Types of pineapple fibers
- Li Nuan: it is called good fiber.
- Bastos: Short for coarse fiber
Chemical composite
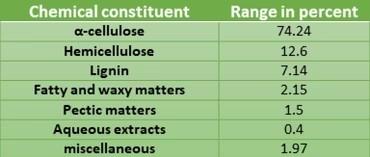
Pineapple fiber properties
Features of pineapple fiber: Minority (tex): 2.44-3.56 Fiber strength (g/tex): 30.00-51.00 Length%: 2.5-3.5 Moisture absorption%: 11.5-12.00 elasticity dyn / cm2: 3.80 Rotational hardness dyn / cm2 x 1010: 0.36 Moisture (weight percent): 11.8 Young’s modulus (GPa): 34.5-82.51 Specific strength (GPa/g/cm3): 0.3-1.1 Specific modulus (GPa / g / cm3): 22.7-54.3 Initial modulus (cN / tex): 570-700 Break length (%): 1.6-3 It has high insulation and absorption power. The thermal conductivity of this fiber is 0.0273 watt/m2/k, which indicates that these fibers can be used as a good heat insulator. It has higher tensile strength and torsion than cotton fibers. It has a high degree of crystallinity with a spiral angle of 15 ͦ.
Alkali effect: length decreases when used with 18% NaOH, length increases with solution. Effect of H2O2: H2O2 increases strength by 5% to 6% but reduces strength by 40% to 45%. Pine fiber dissolves in 60% sulfuric acid within 5 minutes.
Characteristics of pineapple fibers
- Pineapple fiber is soft, elastic, white or ivory-coloured, and shiny.
- Pineapple shreds are considered the queen of Filipino seeds.
- It integrates well into another website.
- Pina jewellery is called Pina calado.
- When pineapple fiber is woven into silk form, it is called pineapple silk or pineapple silk.
- A mixture of abaca and silk is called Pina jusi.
- It is 10 times stronger than cotton and its fibers and is able to absorb more dyes due to its higher moisture content.
- It can be dyed with direct dyes, transfer dyes, vat dyes and azo dyes and is faster than cotton dyeing.
- Due to the presence of lignin and hemicellulose, more than 15% amorphous and acidic properties, it can reach dyes that require heat treatment.
Uses of pineapple leaf fiber
- Pineapple fibres can be used in many different sectors, from clothing to technical fibres.
- They are used in industrial applications such as tyres and conveyor belts and can also be used in the paper industry.
- Pineapple fabric is used to make upholstery and furniture.
- It is used to make table linen, bags, mats and other clothing.
- Sporting goods, luggage, cars, cupboards and mats.
- Surface modified PALF is used to make mechanical parts such as belts, conveyor cords, transmission fabrics, airbag pull cords, etc.
- It is often used to make yarns for textiles.

